BOGGLE 보글 게임 / ALGOSPOT
문제링크 : https://algospot.com/judge/problem/read/BOGGLE
제출링크 : https://algospot.com/judge/submission/detail/653737
자바소스 : https://github.com/skysign/WSAPT/blob/master/ALGOSPOT/BOGGLE/src/Main.java
DP로 풀어야 하는 문제입니다. exhaustive search 전부다 찾으면, 시간이 너무 오래 걸림니다.
게임판이 모두 a 로 채워저 있고, 찾아야하는 단어가 aaaaab 라고 한다면,
- exhaustive search로 찾을 때, 모든 칸을 방문합니다.
- 마지막에 b 가 없어서 찾지 못하고, NO를 출력합니다.
문제 처음에 풀때, Recurrence relation를 어떻게 잡아야 하는지 고민을 좀 했었던 문제입니다.
게임판의 크기 : M x N 이라고 하면
게임판의 (0, 0)에서 처음으로 찾을 때는, exhaustive search 방법으로 찾는 것과 동일합니다.
하지만, (0,1)에서 (0,0)에서 방문했던 곳을 또 방문할 필요는 없습니다.
이렇게 하기 위해서는 아래와 같이 recurrence relation을 정의할 수 있습니다.
dp_{i,j,k} = k
단어의 K번째 글짜를 지나갈 때, 게임판의 (i,j) 방문했다.
이렇게 정의 하기 위해서는 dp는 M x N x '단어의 길이' 크기의 DP 배열이 이어야 합니다.
이제 부터는 방문하기 전에, dp 를 먼저 확인해 볼 필요가 있습니다.
dp_{i,j,k}가 0 인 위치만 방문하고, 0이 아닌 숫자가 있다고, 방문하려고 했던 순서가, k번 인대, 이미 한번 방문했던 곳이기 때문에, 방문하지 않습니다.
이런 식으로 DP를 사용하면, 중복된 방문을 줄일 수 있기 때문에, exhaustive search보다 빠른 속도로 탐색이 가능합니다.

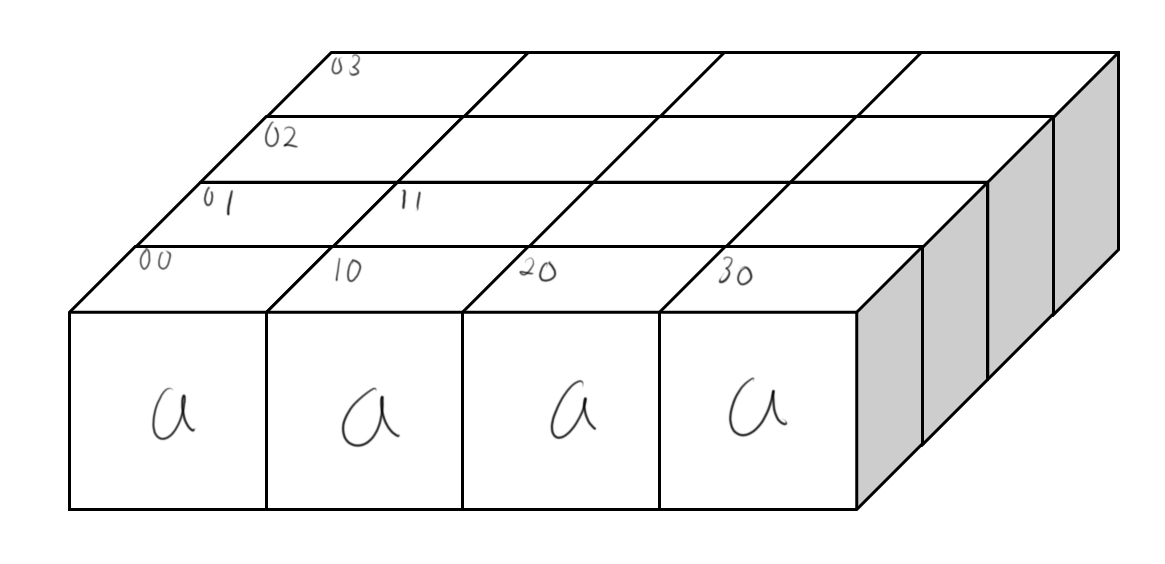
게임판 모두 a로 채워저 있고, 단어가 aaaab라고 한다면, 위의 그림 처럼, (0,0)에서 시작해서 (1,0)을 지나 (2,0)으로 지나갈 수 있습니다. 지나간 위치와, 순서에 따라서, dp에는 아래와 같이 지나간 순서가 남게 됩니다.
- dp_{0,0,0} = 0
- dp_{1,0,1} = 1
- dp_{2,0,2} = 2
이제 (2,0)에서 다시 aaaab를 찾기 시작한다고 하고, (1,0)을 방문하기 위해서, dp_{1,0,1} 을 방문해 봤더니, 1로 적혀있습니다.
따라서 방문할 필요가 없습니다. 이런 식으로 DP를 사용하면, 중복해서 방문하는 횟수를 줄 일 수 있습니다.
최초에 (0,0)에서 찾는 횟수는 DP를 사용하더라도, exhaustive search 와 동일합니다만, 이후 (1,0)에서 출발하는 경우 부터는 (0,1)에서 방문했던 곳들은 중복 방문하지 않게 되면서, exhaustive search보다 빠른 속도로 탐색이 가능합니다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위한 점화식을 정의할 때, '답을 찾았다/못 찾았다가 아니라', '단어의 몇번째 글자에서 방문했었다' 로 점화식을 정의해서, 3차원 배열로 방문했던 순서를 기록해 두는 것이 이 문제를 해결하는대 있어 가장 중요한 점 입니다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* BOGGLE 보글 게임 / ALGOSPOT
* 문제링크 : https://algospot.com/judge/problem/read/BOGGLE
* 제출링크 : https://algospot.com/judge/submission/detail/653737
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main main = new Main();
main.getInput();
}
public void getInput() throws IOException {
// Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Reader sc = new Reader();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int T = sc.nextInt();
// sc.nextLine();
for(int t=0; t<T; ++t) {
char[][] map = new char[5][5];
int M = 5;
int N = 5;
for(int i=0; i<M; ++i) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
for(int j=0; j<N; ++j) {
map[i][j] = line.charAt(j);
}
}
int cntWords = sc.nextInt();
String[] words = new String[cntWords];
// sc.nextLine();
for(int i=0; i<cntWords; ++i) {
String word = sc.nextLine();
boolean b = findWord(map, M, N, word, 0);
// System.out.printf("%s %s\n", word, (b)? "YES": "NO");
String ans = word + " ";
ans += (b)? "YES": "NO";
ans += "\n";
bw.write(ans);
}
}
bw.close();
}
public boolean findWord(char[][] map, int M, int N, String word, int idxWord) {
boolean[][][] visitiedMap = new boolean[M][N][word.length()];
for(int i=0; i<M; ++i) {
for(int j=0; j<N; ++j) {
if(findWord2(map, M, N, i, j, word, idxWord, visitiedMap))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean findWord2(char[][] map, int M, int N, int i, int j, String word, int idxChar, boolean[][][] visitedMap) {
int[] dis = new int[]{-1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0};
int[] djs = new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1};
visitedMap[i][j][idxChar] = true;
if(word.charAt(idxChar) != map[i][j])
return false;
if(idxChar == (word.length()-1))
return true;
for(int k=0; k<dis.length; ++k) {
int di = i + dis[k];
int dj = j + djs[k];
if((0<= di) && (di < M) && (0<=dj) && (dj < N)) {
if(visitedMap[di][dj][idxChar+1]) {
continue;
}
if(findWord2(map, M, N, di, dj, word, idxChar+1, visitedMap))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/fast-io-in-java-in-competitive-programming/
class Reader
{
final private int BUFFER_SIZE = 1 << 16;
private DataInputStream din;
private byte[] buffer;
private int bufferPointer, bytesRead;
public Reader()
{
din = new DataInputStream(System.in);
buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
bufferPointer = bytesRead = 0;
}
public Reader(String file_name) throws IOException
{
din = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file_name));
buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
bufferPointer = bytesRead = 0;
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException
{
byte[] buf = new byte[64]; // line length
int cnt = 0, c;
while ((c = read()) != -1)
{
if (c == '\n')
break;
buf[cnt++] = (byte) c;
}
return new String(buf, 0, cnt);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException
{
int ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ')
c = read();
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg)
c = read();
do
{
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
} while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg)
return -ret;
return ret;
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException
{
long ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ')
c = read();
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg)
c = read();
do {
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
}
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg)
return -ret;
return ret;
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
double ret = 0, div = 1;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ')
c = read();
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg)
c = read();
do {
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
}
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (c == '.')
{
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9')
{
ret += (c - '0') / (div *= 10);
}
}
if (neg)
return -ret;
return ret;
}
private void fillBuffer() throws IOException
{
bytesRead = din.read(buffer, bufferPointer = 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (bytesRead == -1)
buffer[0] = -1;
}
private byte read() throws IOException
{
if (bufferPointer == bytesRead)
fillBuffer();
return buffer[bufferPointer++];
}
public void close() throws IOException
{
if (din == null)
return;
din.close();
}
}
}